Japan car makers crank up automation, MIT and Nvidia researchers develop rapid-response algorithm for robots, and more
Daily brief on news from the world of automated mobile robots.
Japanese automotive industry hits five-year high in automation
Japan’s automotive industry installed approximately 13,000 industrial robots in 2024, marking an 11 percent increase from the previous year and reaching the highest level since 2020. This surge is driven by a sector-wide shift toward alternative powertrains, with manufacturers investing in battery-electric, fuel cell, and hydrogen-fuelled vehicles.
The industry’s robot density reached 1,531 per 10,000 employees in 2023, ranking fourth globally. Robotics adoption not only supports flexible production but is also seen as key for Japan’s broader societal advancement.
Vention launches next-gen modular palletizer for end-of-line automation
Vention has unveiled an updated Rapid Series Palletizer designed to accelerate end-of-line automation solutions. The new system supports vertical stacking of multiple product types, enabling fast relocation and easy software integration for custom pallet recipes.
Compatible with both collaborative and industrial robots, the palletizer offers real-time diagnostics, 24/7 video support, and modular hardware for scalability—streamlining deployment and performance tracking in warehouse and manufacturing environments.
Compacting and mobilizing robots are showcased at Automate 2025
At Automate 2025, manufacturers highlighted compact and mobile robots designed for better integration with existing factory layouts. Notably, Techman Robot’s cobots — with integrated vision systems — work collaboratively with AMRs for flexible material handling and inspection.
Ericsson demonstrated how private industrial 5G enables inventory-counting by drones tethered to AMRs, showcasing advanced communications as key to expanding mobile robotics use cases in logistics and manufacturing.
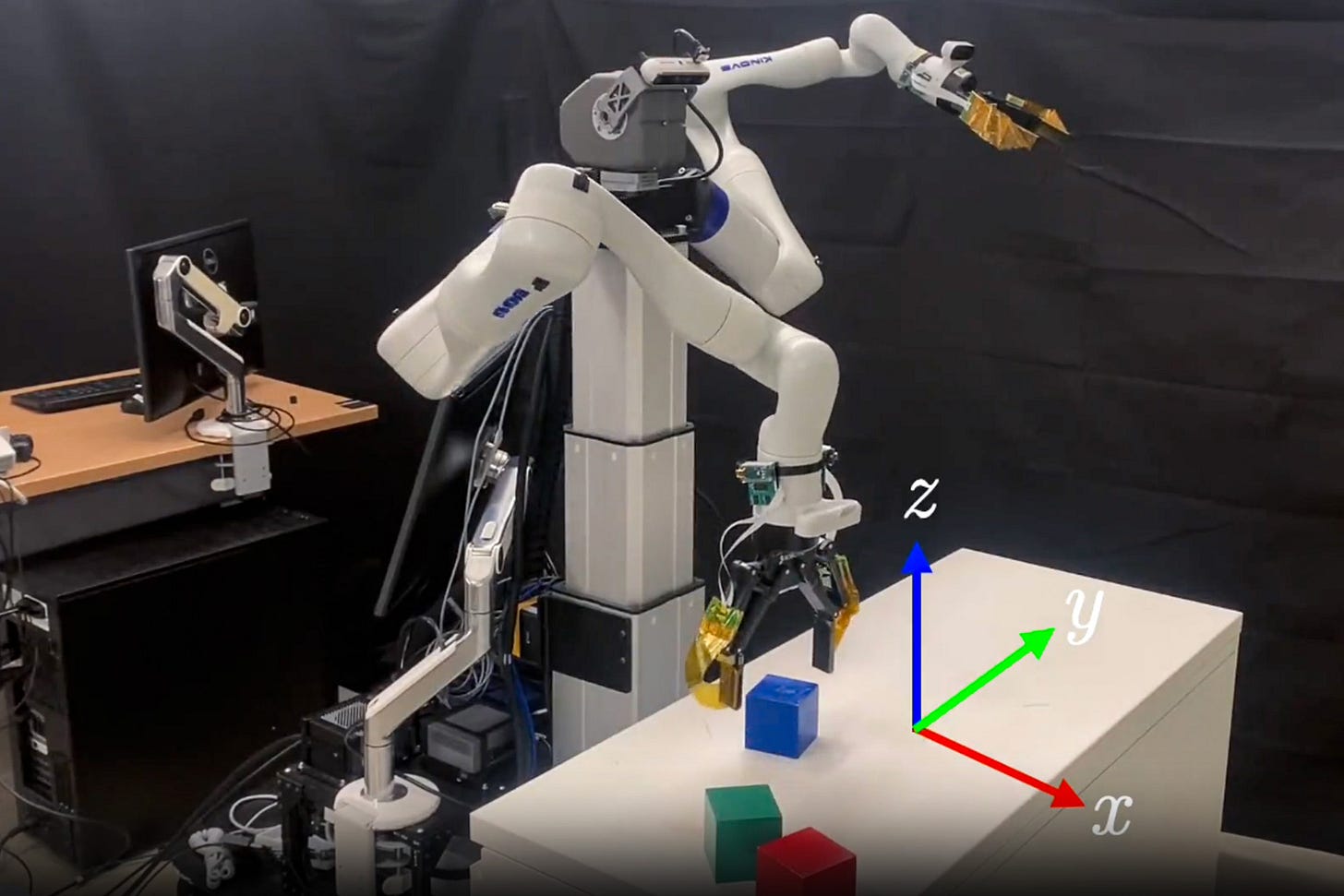
New system enables robots to solve manipulation problems in seconds
A team from MIT and NVIDIA Research has introduced an algorithm called cuTAMP that allows robots to rapidly plan and execute complex manipulation tasks. Traditional robot planning methods examine actions one by one, but cuTAMP leverages GPU-powered parallel processing to consider and optimize thousands of possible solutions at once.
This breakthrough enables robots to solve intricate tasks, such as packing varied objects without collisions, in mere seconds rather than minutes. The technique functions without training data and performs consistently across multiple robot platforms, paving the way for broader and faster deployment in dynamic environments like warehouses and factories.
The developers aim to further integrate language and vision models, so robots can respond to voice commands and new tasks in real time.


